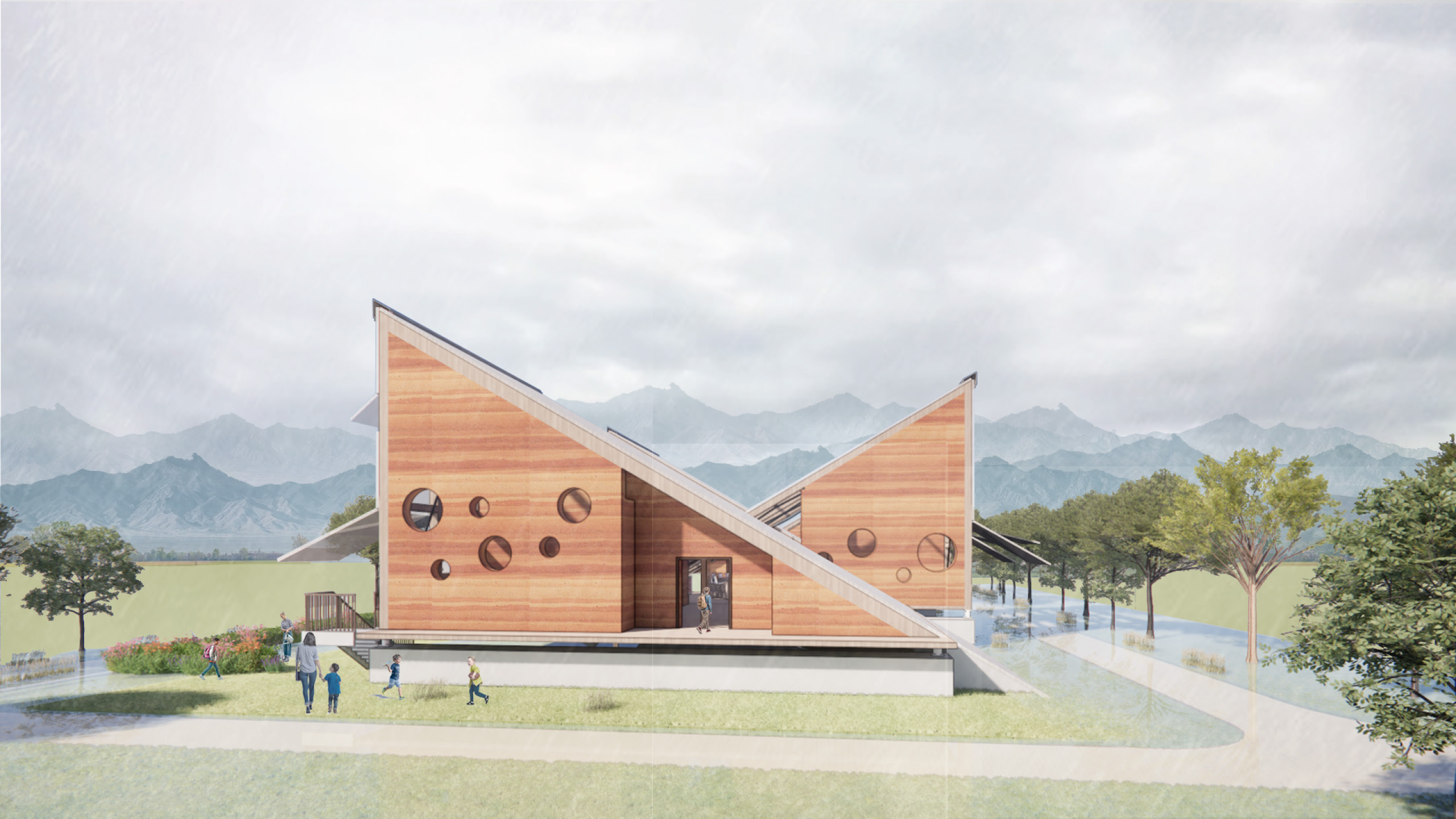
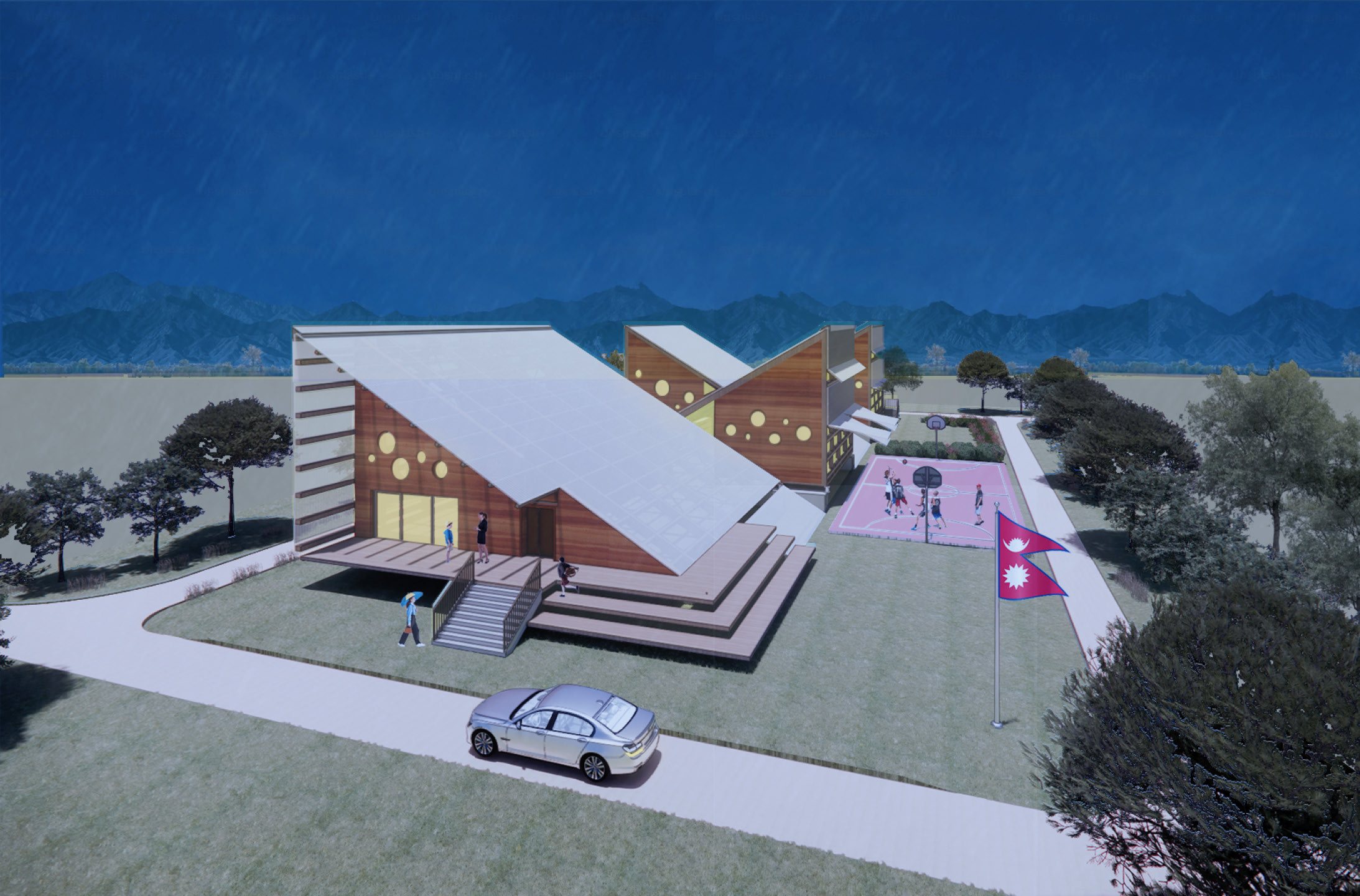
The design proposal aims to inspire and educate students while also serving the surrounding community
This school provides a haven during emergencies and explores the possibilities of creating an inspiring and comfortable learning environment. It addresses technical challenges related to seismic activity and monsoons.


Credit – Renderings: @stead_arch
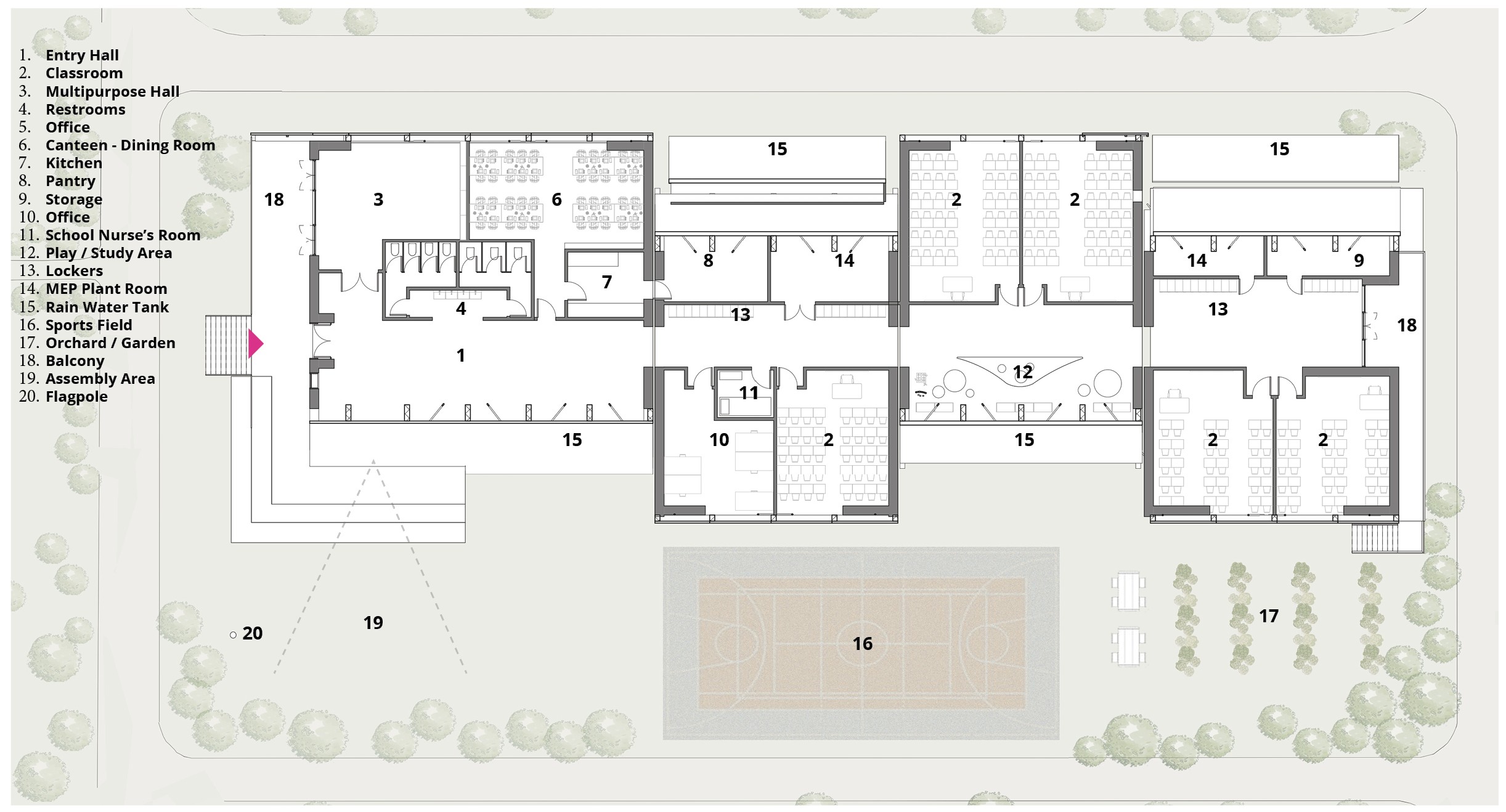
NEPAL FLAGSHIP SCHOOL
The design proposal aims to inspire and educate students while also serving the surrounding community. This school provides a haven during emergencies and explores the possibilities of creating an inspiring and comfortable learning environment. It addresses technical challenges related to seismic activity and monsoons.
Simple and Elegant Materials, Regionally Sourced, Designed for Safety
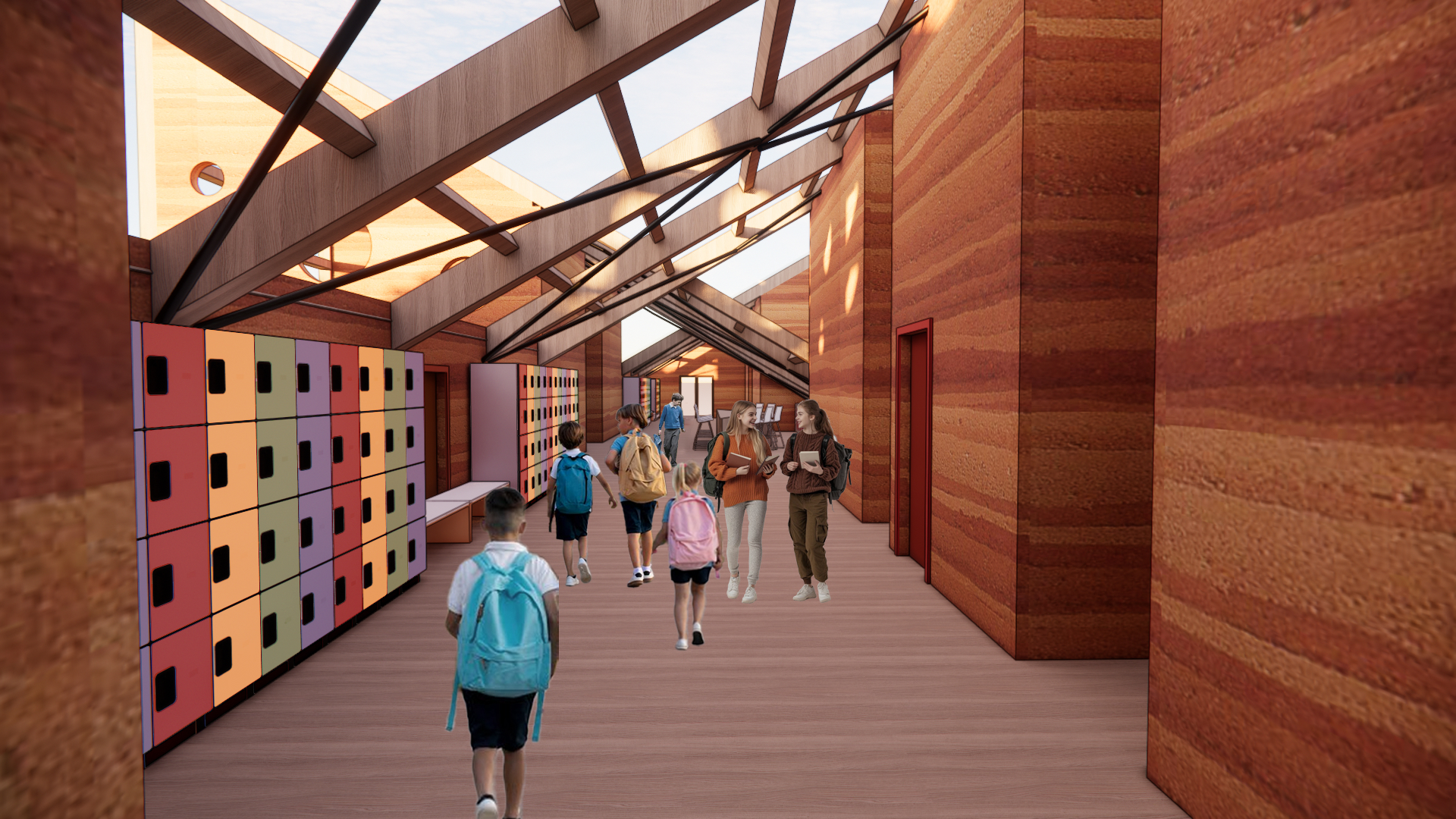
Intended to inspire and support the community
Background
School Program
The school will accommodate 200 students aged 3 to 14.
The design must be modular, allowing for construction in phases as
funding becomes available or needs arise, while maintaining functionality
and coherence.
Sustainability
Reduced Carbon Emissions: Local materials like bamboo, and rammed earth require less energy for transportation and production compared to imported materials like concrete and fired bricks.
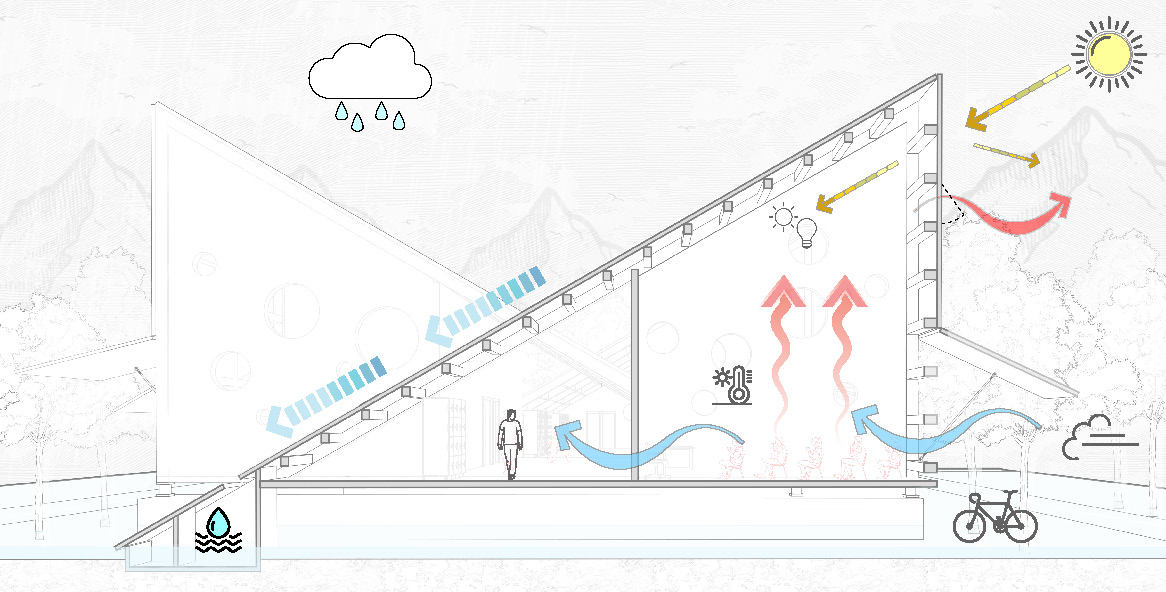
Water Collection:
Sloped roofs feature water collection tanks for rainwater, which can be filtered and used for waste management and gardening.
Passive Cooling:
Operable panels at the roof pitch allow heat to escape in summer, creating a cooling ventilation system when combined with ground floor windows.
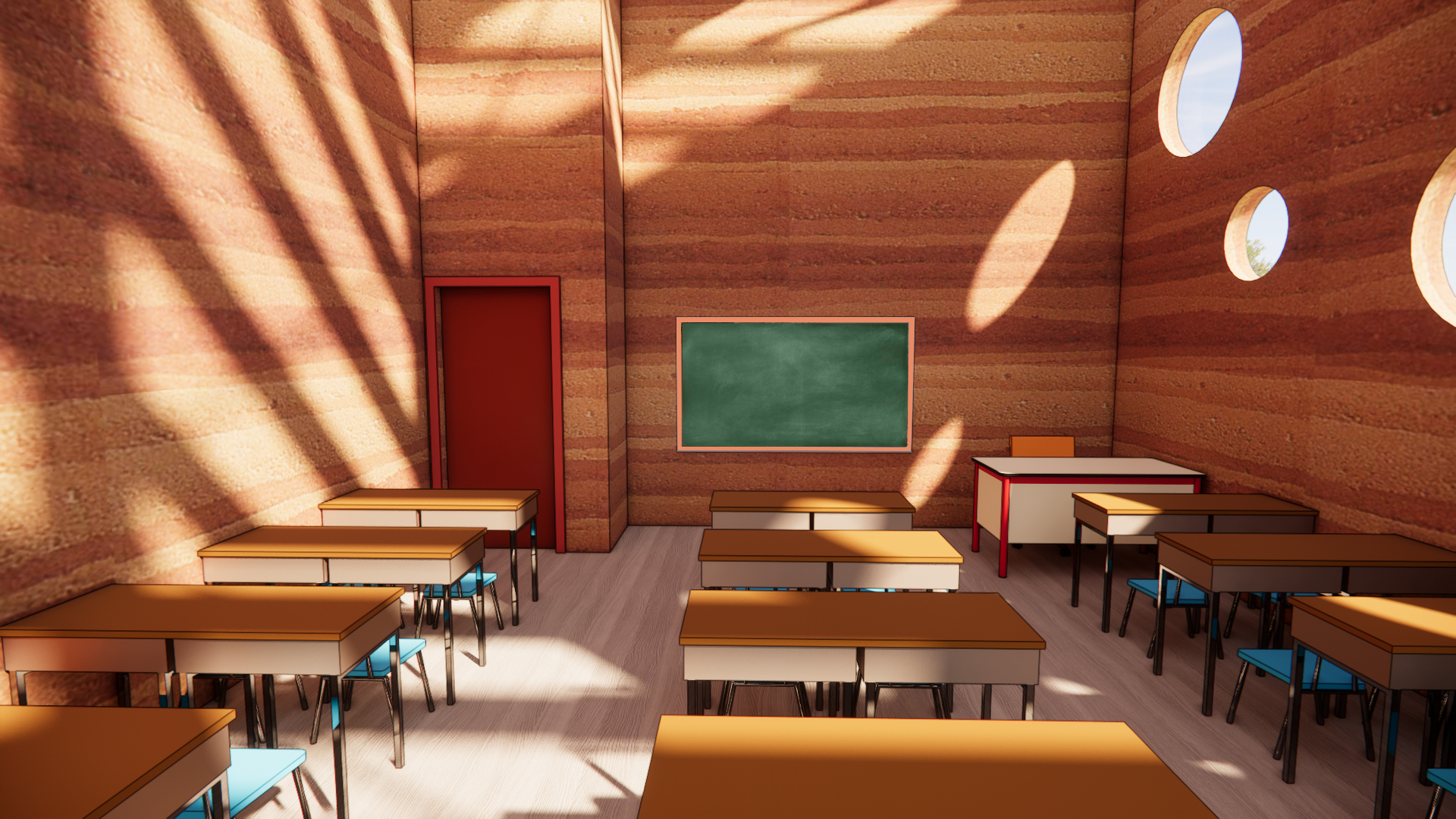
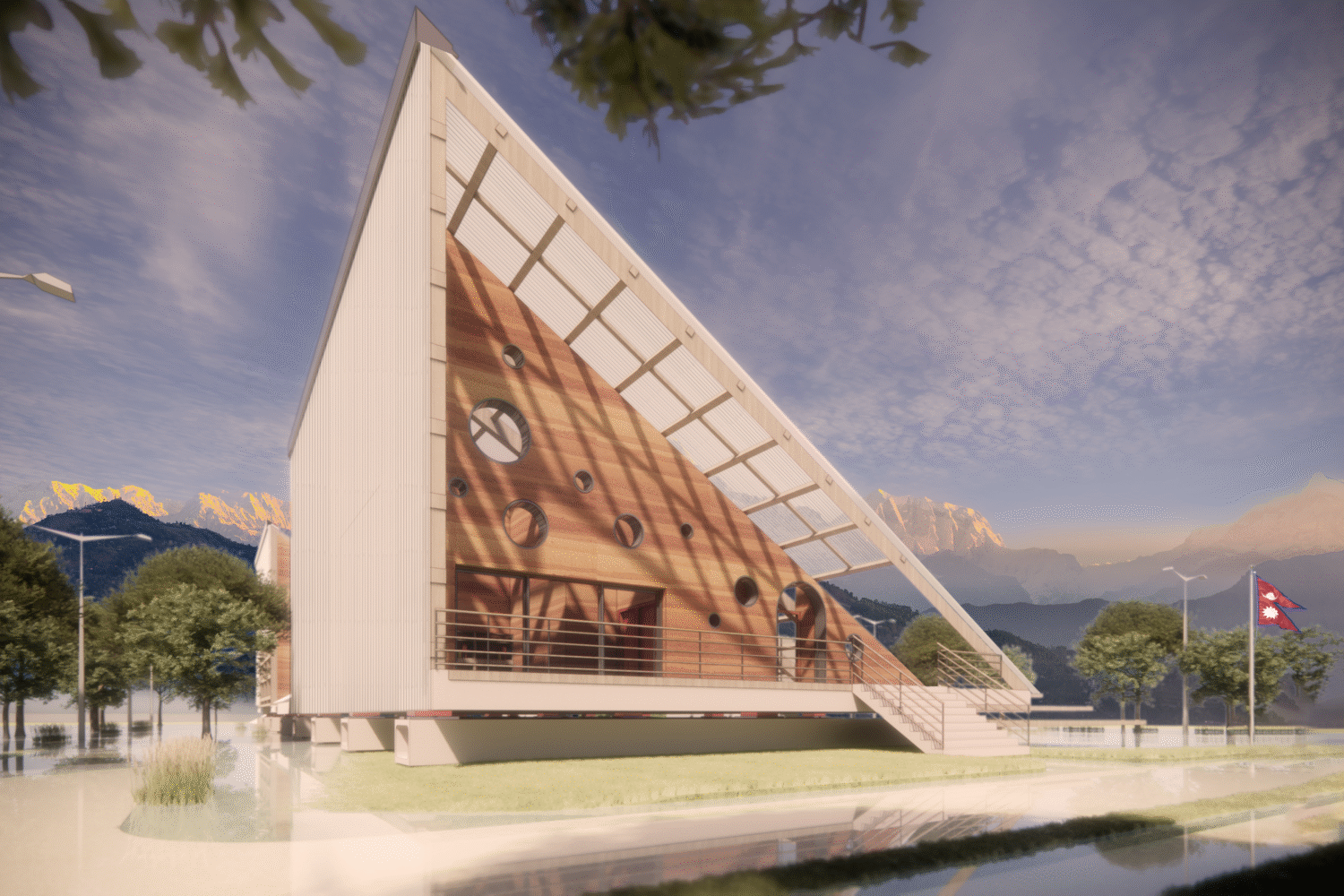
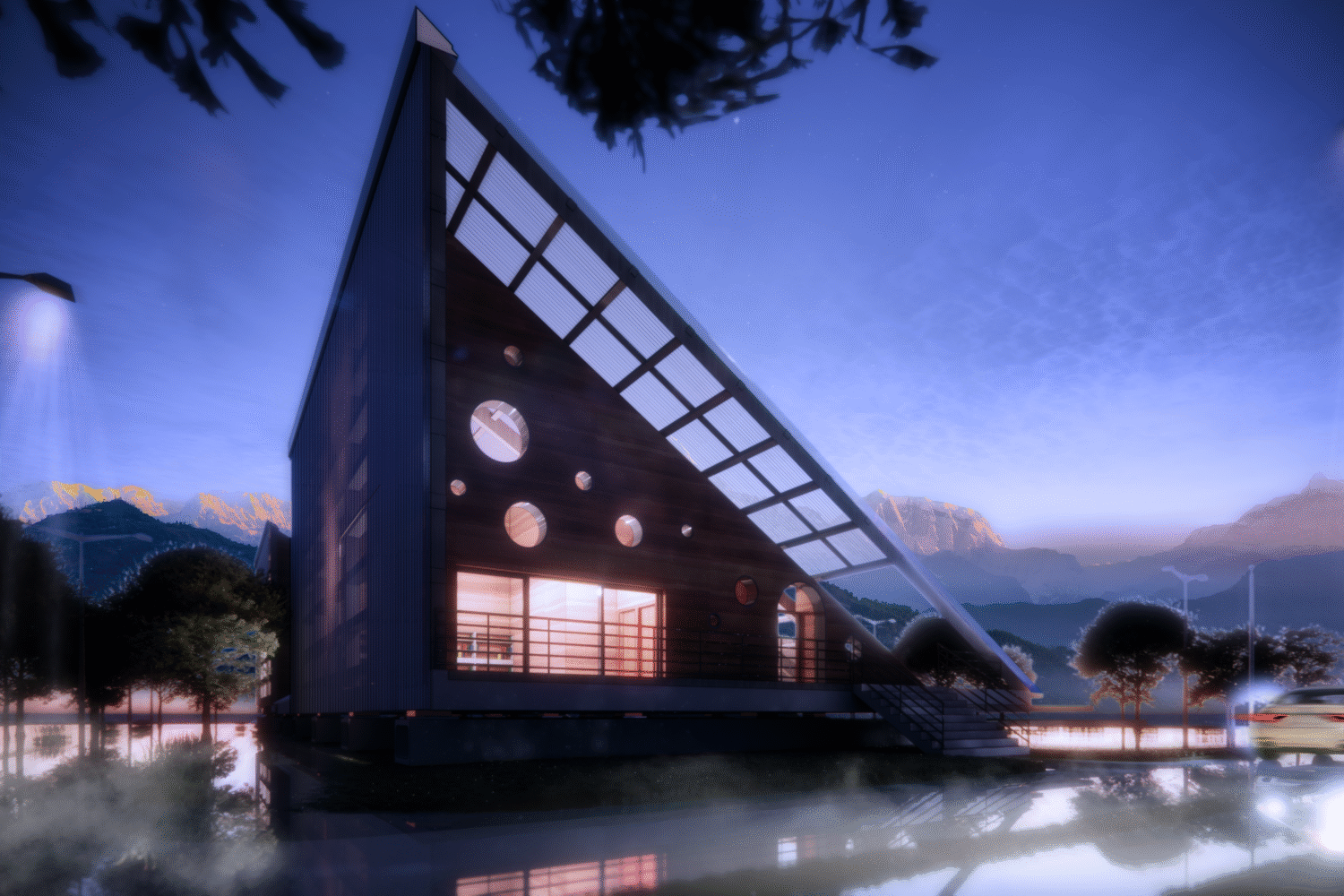
The Design
Materials
The school primarily uses timber, rammed earth, and polycarbonate. Monsoon Design Monsoon resilience is integrated with seismic solutions:
Rammed Earth:
Rammed earth is easily sourced and created locally, reducing the carbon footprint. The circular windows add a touch of playfulness while also allowing direct sunlight to enter each of the main spaces.
Polycarbonate:
Polycarbonate roofs provide natural filtered daylight without glare and offer insulative properties. Lightweight and easily transported, they enhance sustainability.
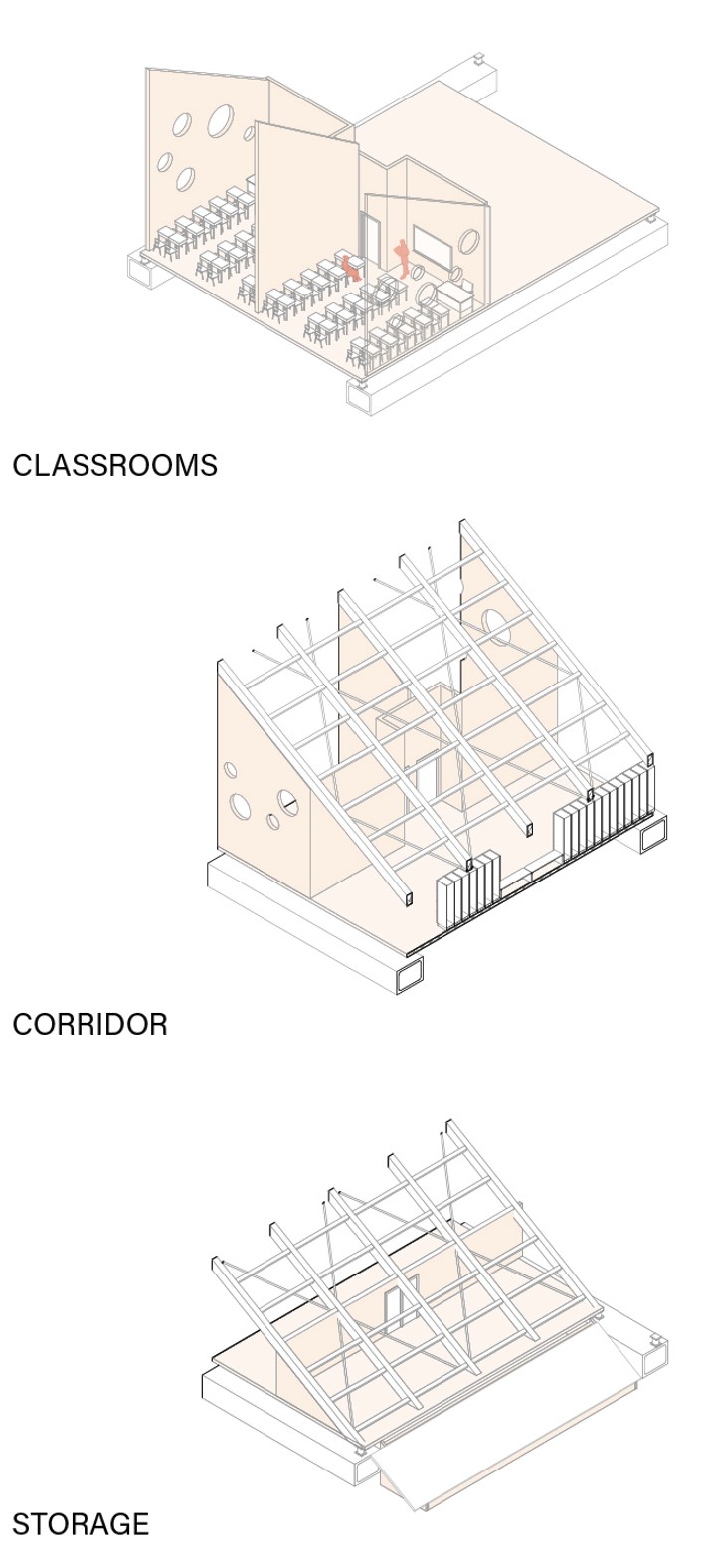
Timber:
Local timber and bamboo are used for battens and small sub-structure members with smaller spans.
Structure
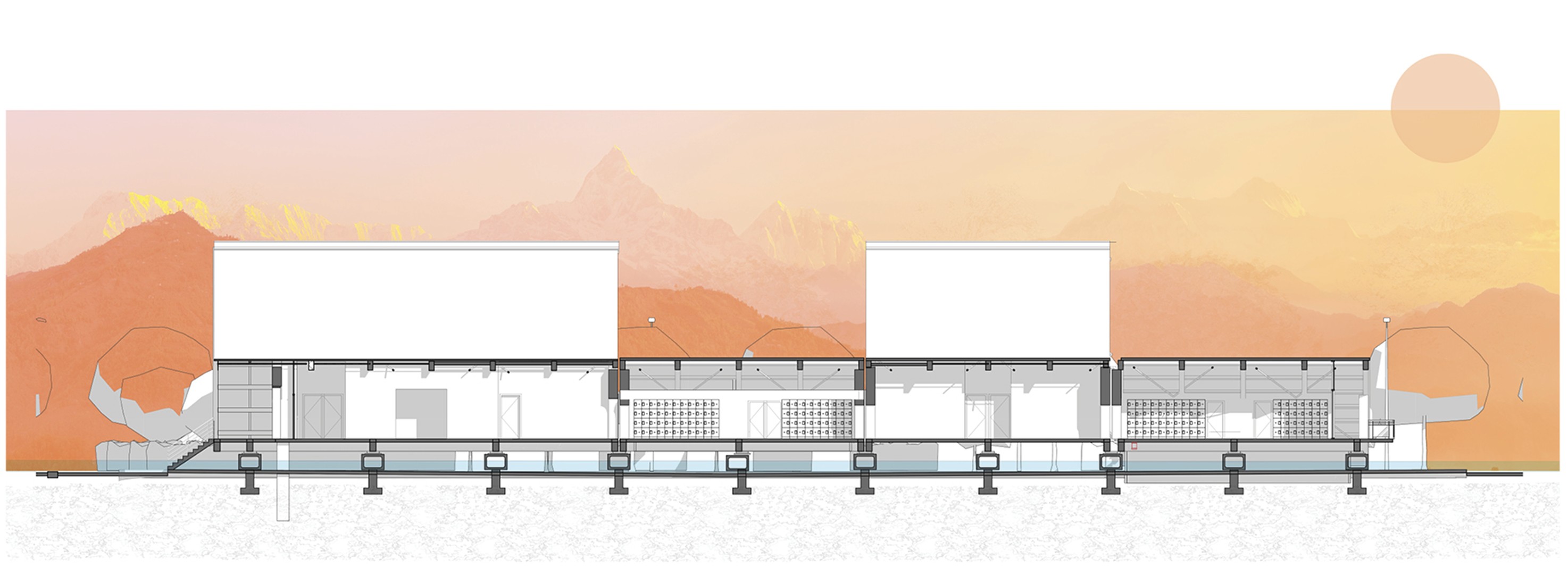
The proposal utilizes a combination of timber and bamboo frames along with rammed earth structural walls as its primary construction materials.
Each section of the building features a double rammed earth wall. Specially designed to mitigate cracking during seismic movements, enhancing the overall stability an safety of the structure.
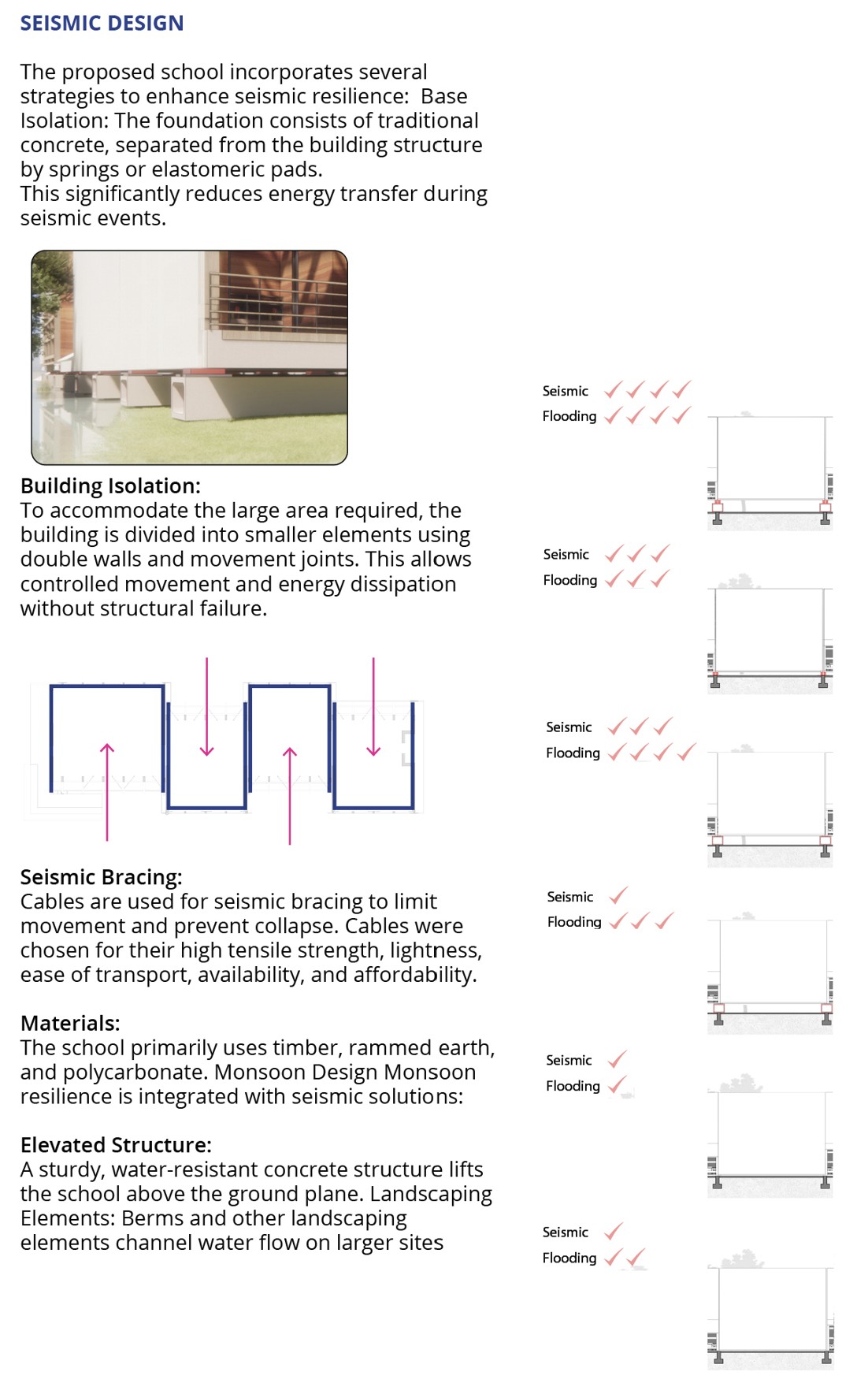
Seismic Design
The proposed school incorporates several strategies to enhance seismic resilience:
Base Isolation: The foundation consists of traditional concrete, separated from the building structure by springs or elastomeric pads. This significantly reduces energy transfer during seismic events.
Building Isolation:
To accommodate the large area required, the building is divided into smaller elements using double walls and movement joints. This allows controlled movement and energy dissipation without structural failure.
Seismic Bracing:
Cables are used for seismic bracing to limit movement and prevent collapse. Cables were chosen for their high tensile strength, lightness, ease of transport, availability, and affordability.
Monsoons – Elevated Structure:
A sturdy, water-resistant concrete structure lifts the school above the ground plane. Landscaping Elements: Berms and other landscaping elements channel water flow on larger sites
Area:
355m² (3,800 sqft)
Floors:
1
Materials:
Rammed Earth, Timber Structure, Bamboo, Polycarbonate, Isolation Springs
Competition Entry
Semifinalist
Scope:
Architect
Link: